(Also available in WeScheme)
Students learn to read function notation and evaluate expressions using function definitions, tables, and graphs. Students also describe the order of operations involved in algebraic function compositions such as f(g(h(x)))
Lesson Goals |
Students will be able to:
|
Student-Facing Lesson Goals |
|
Prerequisites | |
Materials |
This lesson is unplugged, and does not require a computer.
|
Supplemental Materials |
|
Preparation |
|
🔗Function Notation (Definitions) 15 minutes
Overview
Students connect their understanding of function definitions in Pyret to function definitions in math.
Launch
We’ve seen how functions like gt can be defined, and then applied to a number to create a green triangle. And once gt is defined, we can use it with many different numbers to create many different triangles - all without having to write out "solid", "green", etc.
But how does this function work?
When we apply a function to some inputs, we substitute those inputs for the variables in the definition. In the example below, the inputs are substituted for the variable size in the body of the gt function.
fun gt(size): triangle(size, "solid", "green") end
| Apply the Function | Substitute the Input(s) | Compute the Answer |
|---|---|---|
gt(10) |
triangle(10, "solid", "green") |
|
gt(20) |
triangle(20, "solid", "green") |
|
gt(30) |
triangle(30, "solid", "green") |
|
gt(40) |
triangle(40, "solid", "green") |
|
gt(50) |
triangle(50, "solid", "green") |
|
Let’s take a look at a function that works with Numbers:
fun f(x): x + 8 end
| Apply the Function | Substitute the Input(s) | Compute the Answer |
|---|---|---|
f(10) |
10 + 8 |
18 |
f(20) |
20 + 8 |
28 |
f(30) |
30 + 8 |
38 |
f(40) |
40 + 8 |
48 |
f(50) |
50 + 8 |
58 |
Once again, the input is substituted for the variable.
You’ve already seen that Pyret looks a little different from traditional math, even if it behaves the same way.
Math books use something called Function Notation to define functions. Here’s a side-by-side comparison of the same function, in Pyret and in function notation:
| Defining Functions in Pyret | Defining Functions in Function Notation |
|---|---|
fun f(x): x + 8 end |
f(x) = x + 8 |
-
What do these forms have in common?
-
Both forms show the name of the function, as well as the names of the variables. They also show what the function does with those variables.
-
-
How are these forms different from one another?
-
In Pyret, we use a colon instead of an equals sign. In Pyret, we see fun at the beginning and end at the end.
-
In math - just as in programming - we compute the value of the expression for any specific input by substituting numbers for the variable(s) used in the definition, just as we did with gt.
Investigate
-
Start by looking at each table and highlighting what is changing from the first row to the following rows.
-
Then, match each table to the function that defines it.
You may also want to have students complete Matching Examples & Function Definitions - Math (Desmos)
-
Turn to Function Notation - Substitution.
★ For more challenging function notation evaluation exercises direct students to Function Notation Challenge.
Synthesize
You can think of f(3) as a question.
-
What question is it asking you to evaluate?
-
What is the value of x + 8 when x is 3?
-
-
What is another way you can ask it?
-
What is 3 + 8?
-
🔗Function Notation (Graphs) 15 minutes
Overview
Students will learn to connect function definitions to Graphs.
Launch
-
If f(x) = x - 5, what is the value of f(7), and why?
-
2. Because if we substitute 7 for x we get 7 - 5 = 2
-
-
What is the value of f(8)?
-
3. Because if we substitute 8 for x we get 8 - 5 = 2
-
-
What is the value of f(9)?
-
4
-
For each of these inputs, we have an output. If we graph each input-output pair on the coordinate plane, we can "see" the function as a line on a graph.
Let’s take a look at the graph of f(x) = x - 5.
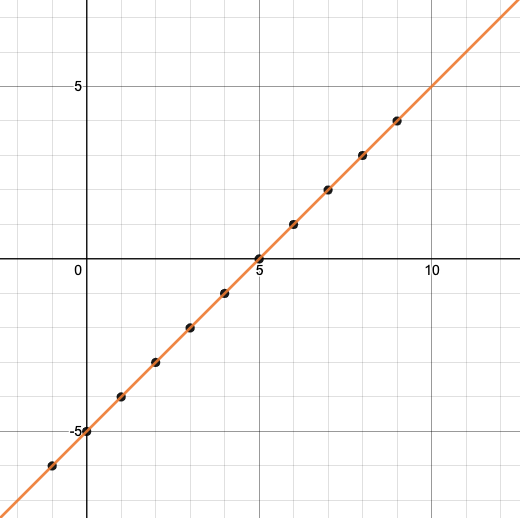
-
How could we have determined that f(7) = 2 from looking at the graph, if we hadn’t started with the function definition?
-
We could have looked for a point whose y-coordinate was 2. This would lead us to the point (7, 2), which tells us that the output of the function when x is 7 is 2.
-
-
From looking at the graph, what is the value of f(3)?
-
-2
-
-
What other values on this graph could we describe using function notation?
-
Answers will vary. For example: f(0) = - 5 or f(0.5) = - 4.5
-
Even if we can’t see the definition of a function, we can reason about it just by looking at the graph!
Let’s look at the graph below, which shows only a few points on the line drawn by a function:
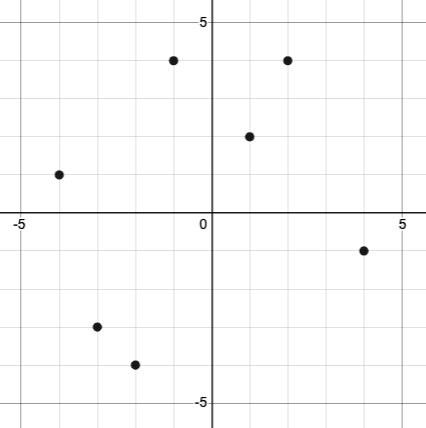
-
From looking at the graph, what is the value of f( - 2)?
-
-4
-
-
What is the value of f(1)?
-
2
-
-
What is the value of f(3)?
-
There isn’t one! It’s undefined.
-
-
What other values on this graph could we describe using function notation?
-
Answers will vary. For example, f( - 1) = 4 or f(2) = 4
-
Optional: Piecewise Functions
When evaluating an expression for a piecewise function, points on the graph marked with hollow circles are boundary points, but not part of the solution set, so we ignore them and focus on the solid points. For example, on the graph below, when evaluating f(2), we ignore the hollow point at (2, 4) and focus on the solid point at (2,3), so f(2) = 3.
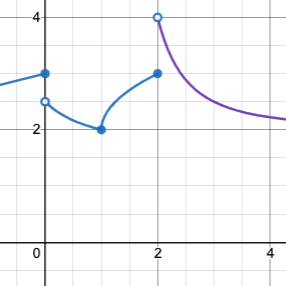
What is the value of f(0) in the graph above? 3
Investigate
Complete Function Notation - Graphs.
If your students are ready for a challenge (piecewise functions!), have them work on Function Notation - Piecewise Graphs.
Synthesize
-
Can you think of any values that it would be difficult to determine from one of these graphs?
-
It would be hard to be precise for many of the points on the graphs that curve. For example, f(4) on the second graph would have to be a decimal value and it’s hard to know exactly what the decimal should be without a function definition to evaluate…
-
🔗Function Notation (Tables) 15 minutes
Overview
Students will learn to connect function definitions to input-output Tables.
Launch
Take a look at the table of input-output pairs that satisfy the function f(x) = x - 5.
x |
-10 |
-5 |
5 |
7 |
13 |
y |
-15 |
-10 |
0 |
2 |
8 |
-
How could we use the table to determine the value of f(7)?
-
We would just look for 7 in the x-column and see that the value beside it is 2.
-
-
What is the value of f( - 10)?
-
-15
-
Investigate
Complete Function Notation - Tables.
Synthesize
-
What did you Notice?
-
What did you Wonder?
-
A few of the tables did not represent functions. Which ones?
-
The last one in the top row, the last one in the middle row and the 3rd one in the bottom row.
-
-
How did the fact that those tables weren’t functions impact our ability to describe a value using function notation?
-
When x appeared more than once in the table and was associated with different outputs, it wasn’t clear what number the expression should evaluate to.
-
🔗Diagramming Function Composition 15 minutes
Overview
The Circles of Evaluation are extended to provide a visual-spatial metaphor for function composition, in addition to Order of Operations.
Launch
Suppose we had the following three function cards for the functions f, g, and h:
-
f multiplied its input by 3
-
g added six to its input
-
h subtracted one from its input
We can compose those functions in any order. If we composed them as f(g(h(x))) and evaluated them for x = 4 what would happen?
We can diagram the function composition using Circles of Evaluation (see first column, below). In the second column, we’ve replaced the function names in each Circle of Evaluation with what each function does:
| Function Composition | Order of Operations |
|---|---|
(f (g (h x))) |
(* 3 (+ (- x 1) 6)) |
The circles show us that in order to evaluate f(g(h(4))))
-
First we would have to evaluate h(4), subtracting 1 from 4 to get 3
-
Then we would evaluate g(3), adding 6 to 3 to get 9
-
Then we would evaluate f(9), tripling 9 to get 27
Investigate
Turn to Diagramming Function Composition to practice writing, translating and evaluating Circles of Evaluation of composed functions.
More practice is available on Function Composition: Matching and Diagramming Function Composition (2).
Synthesize
-
Do f(g(h(x))) and g(h(f(x))) evaluate to the same thing? Why or why not?
-
No, they do not. Order matters!
-
These materials were developed partly through support of the National Science Foundation, (awards 1042210, 1535276, 1648684, 1738598, 2031479, and 1501927).  Bootstrap by the Bootstrap Community is licensed under a Creative Commons 4.0 Unported License. This license does not grant permission to run training or professional development. Offering training or professional development with materials substantially derived from Bootstrap must be approved in writing by a Bootstrap Director. Permissions beyond the scope of this license, such as to run training, may be available by contacting contact@BootstrapWorld.org.
Bootstrap by the Bootstrap Community is licensed under a Creative Commons 4.0 Unported License. This license does not grant permission to run training or professional development. Offering training or professional development with materials substantially derived from Bootstrap must be approved in writing by a Bootstrap Director. Permissions beyond the scope of this license, such as to run training, may be available by contacting contact@BootstrapWorld.org.





